infomer 的使用包括创建和启动两个部分,下面逐步分析这两部分源码
创建 informer
一般情况进行面向 K8s 编程时操作的资源类型往往非常多,不会直接创建某资源的 informer,而是通过 sharedInformerFactory 工厂创建指定资源类型的 informer,这样在多个逻辑里要使用同一类型资源时,可以复用同一份缓存提高性能。
先创建 factory
func NewSharedInformerFactoryWithOptions(client kubernetes.Interface, defaultResync time.Duration, options ...SharedInformerOption) SharedInformerFactory {
factory := &sharedInformerFactory{
client: client,
namespace: v1.NamespaceAll,
defaultResync: defaultResync,
// 保存共享的 informer
informers: make(map[reflect.Type]cache.SharedIndexInformer),
// 记录 informer 是否启动
startedInformers: make(map[reflect.Type]bool),
// 记录 informer 的自定义 resync 参数
customResync: make(map[reflect.Type]time.Duration),
}
// ...
return factory
}从 factory 创建具体资源的 informer
// package informers factory.go
func (f *sharedInformerFactory) Core() core.Interface {
return core.New(f, f.namespace, f.tweakListOptions)
}
// package core interface.go
func New(f internalinterfaces.SharedInformerFactory, namespace string, tweakListOptions internalinterfaces.TweakListOptionsFunc) Interface {
return &group{factory: f, namespace: namespace, tweakListOptions: tweakListOptions}
}
func (g *group) V1() v1.Interface {
return v1.New(g.factory, g.namespace, g.tweakListOptions)
}
// package v1 interface.go
func New(f internalinterfaces.SharedInformerFactory, namespace string, tweakListOptions internalinterfaces.TweakListOptionsFunc) Interface {
return &version{factory: f, namespace: namespace, tweakListOptions: tweakListOptions}
}
func (v *version) Pods() PodInformer {
return &podInformer{factory: v.factory, namespace: v.namespace, tweakListOptions: v.tweakListOptions}
}
// package v1 pod.go
type podInformer struct {
factory internalinterfaces.SharedInformerFactory
tweakListOptions internalinterfaces.TweakListOptionsFunc
namespace string
}
func (f *podInformer) Informer() cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return f.factory.InformerFor(&corev1.Pod{}, f.defaultInformer)
}InformerFor 根据传入的资源类型创建 informer
对于最后的 podInformer.Informer() 中的 factory.InformerFor 实际上就是调用的共享的 sharedInformerFactory.InformerFor,比如传入类型为 pod 它通过反射的到具体的资源类型,判断此资源的 informer 是否已经存在若存在则直接返回,若不存在说明是使用初次获取该 informer,因此使用 newFunc 创建该资源的 informer 并保存到 factory 的 informer map 中。
func (f *sharedInformerFactory) InformerFor(obj runtime.Object, newFunc internalinterfaces.NewInformerFunc) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
// 通过反射的到具体需要的资源类型,如 v1.Pod,查找是在 facotry 中已经存在
// 若存在则无需重新创建,直接返回即可
informerType := reflect.TypeOf(obj)
informer, exists := f.informers[informerType]
if exists {
return informer
}
// 未找到则开始为此资源构建新的 informer,先查找有没有为此资源自定义 resync 时间
// 若没有则使用全局默认的 resync 参数
resyncPeriod, exists := f.customResync[informerType]
if !exists {
resyncPeriod = f.defaultResync
}
// newFunc 构造新的 informer 并加入到 factory
informer = newFunc(f.client, resyncPeriod)
f.informers[informerType] = informer
return informer
}这个用于创建具体资源的 newFunc 是传入的方法,也是在具体资源的实现中定义的,对于 Pod ,这个方法是 NewFilteredPodInformer,源码如下。
NewSharedIndexInformer
func NewFilteredPodInformer(client kubernetes.Interface, namespace string, resyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers cache.Indexers, tweakListOptions internalinterfaces.TweakListOptionsFunc) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).List(context.TODO(), options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).Watch(context.TODO(), options)
},
},
&corev1.Pod{},
resyncPeriod,
indexers,
)
}
// cache.NewSharedIndexInformer
func NewSharedIndexInformer(lw ListerWatcher, exampleObject runtime.Object, defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers Indexers) SharedIndexInformer {
realClock := &clock.RealClock{}
sharedIndexInformer := &sharedIndexInformer{
processor: &sharedProcessor{clock: realClock},
indexer: NewIndexer(DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc, indexers),
listerWatcher: lw,
objectType: exampleObject,
resyncCheckPeriod: defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod,
defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod: defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod,
cacheMutationDetector: NewCacheMutationDetector(fmt.Sprintf("%T", exampleObject)),
clock: realClock,
}
return sharedIndexInformer
}可以看到创建 informer 需要两个关键结构:
cache.ListWatcher这里的 ListWatch 就是使用的原始 clientset 从远程 apiserver ListWatch 方法List(options metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error)Watch(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
cache.Indexer这个是 informer 的本地缓存,从 apiserver 获取的资源对象缓存于此- map of
IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)给定对象找到其索引
- map of
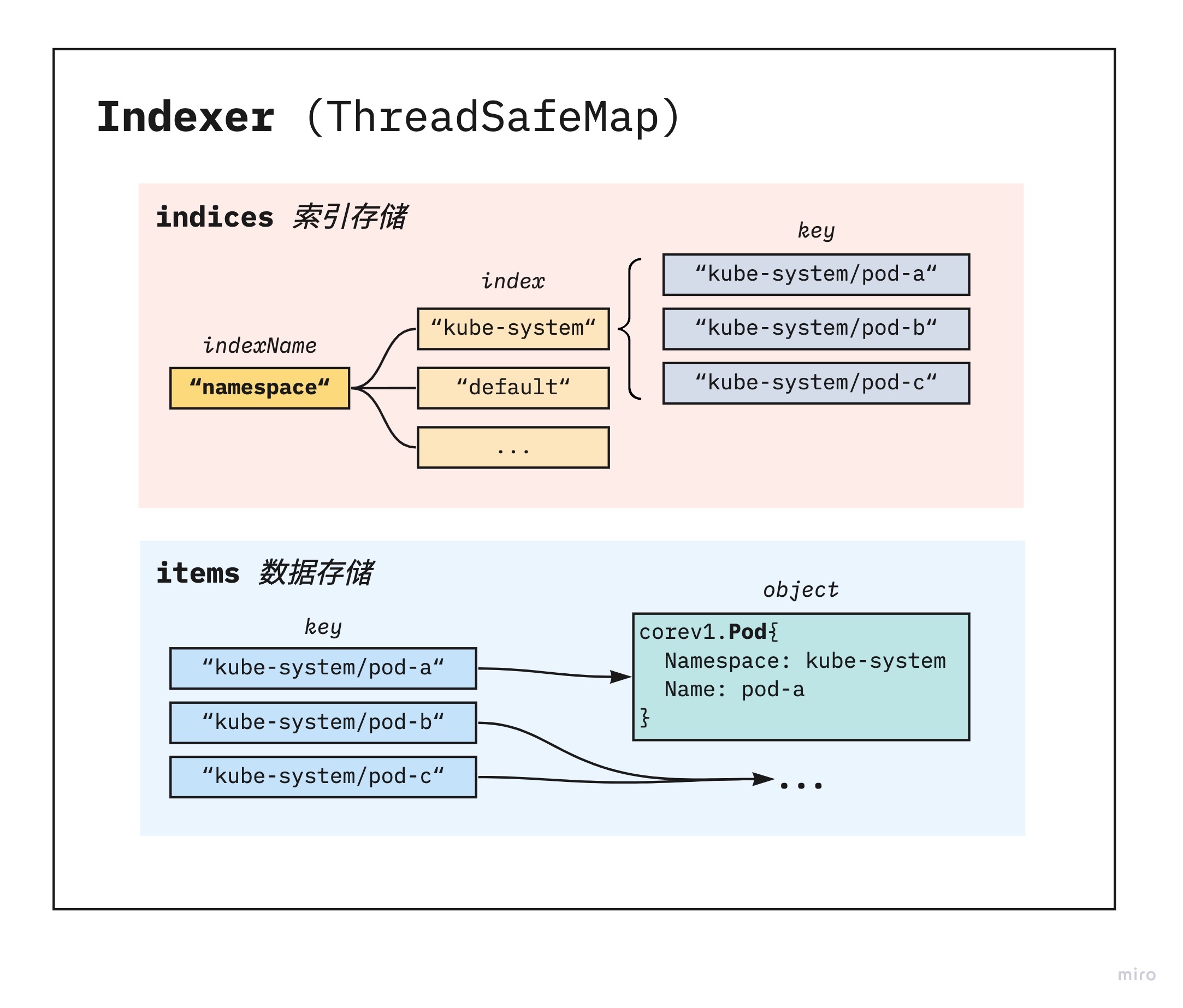
关键结构:Indexer (TreadSafeMap)
Indexer 为 informer 的本地资源缓存数据结构,除了线程安全、map 等基本功能外、它具有一定的索引功能,而 K8s 的资源都是以 namespace 做隔离的,因此 namespace 就是一个简单的索引方式。Indexer 包含两个基本结构:
- indices - 索引存储,当要 list 某 namespace 全量资源时,会先通过 indices 的 namespace 索引找到该 namespace index 下面保存的即为该 index 下的所有资源 key 列表
- items - 数据存储,直接以 map 形式存储,key 为资源的 namespace/name ,value 为整个对象结构体
启动 informer
使用 sharedInformerFactory 创建出来的 informer 不需要独立去启动具体某个 informer,只需要启动 factory 即可,factory 的 Start 方法如下
func (f *sharedInformerFactory) Start(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
for informerType, informer := range f.informers {
if !f.startedInformers[informerType] {
go informer.Run(stopCh)
f.startedInformers[informerType] = true
}
}
}它遍历 factory 下面创建的所有资源类型的 informer 并分别调用其 SharedIndexInformer.Run 方法
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// 构造 DeltaFIFO 队列,cache.Controller 需要此队列
fifo := NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{
KnownObjects: s.indexer,
EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,
})
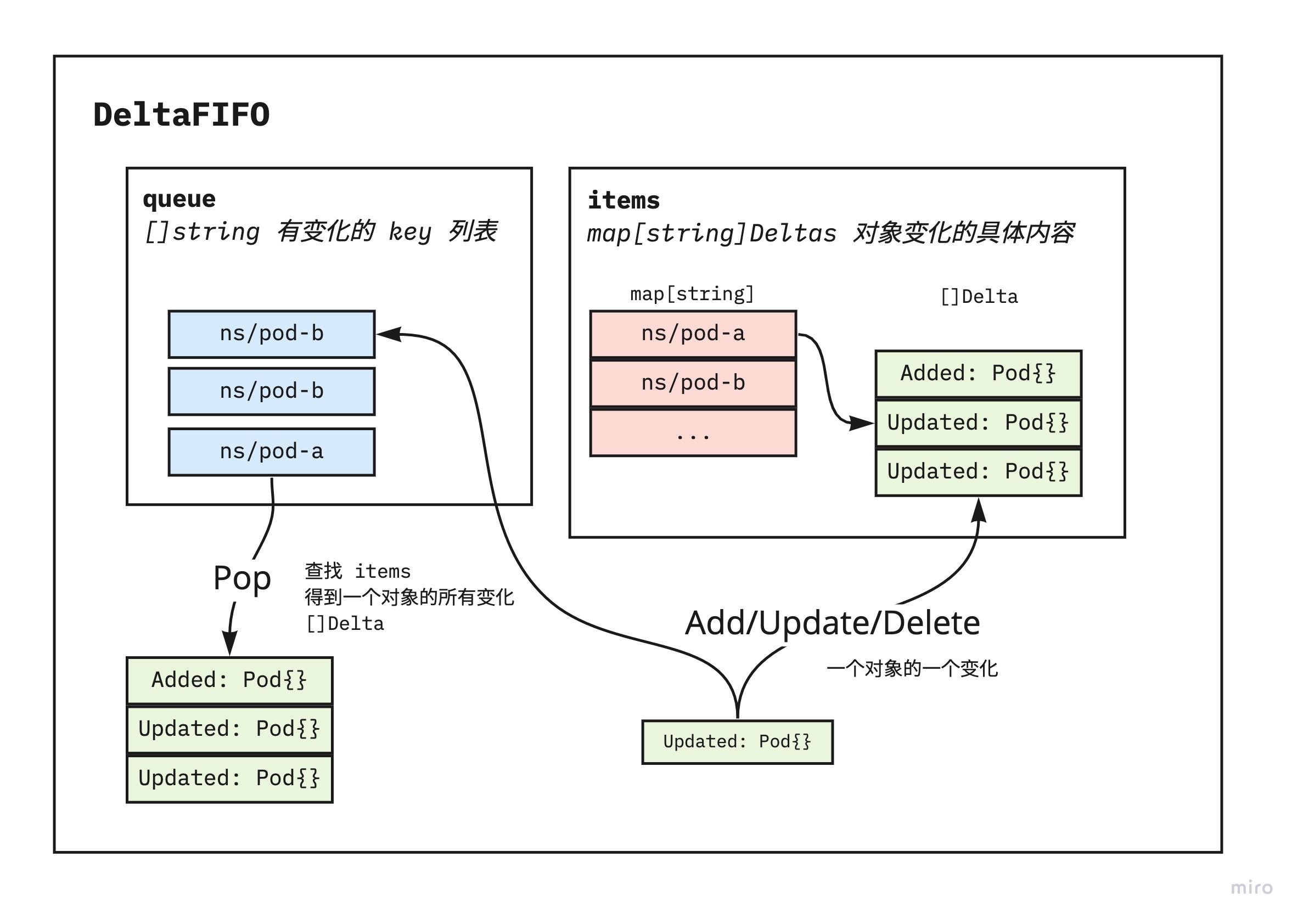
// ...关键结构: DeltaFIFO 队列
func NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(opts DeltaFIFOOptions) *DeltaFIF {
// ...
f := &DeltaFIFO{
// 保存指定 key 资源的变化量
items: map[string]Deltas{},
// 保存有变化事件队列,仅包含变化资源的 key
queue: []string{},
keyFunc: opts.KeyFunction,
knownObjects: opts.KnownObjects,
emitDeltaTypeReplaced: opts.EmitDeltaTypeReplaced,
}
f.cond.L = &f.lock
return f
}
// Deltas 变化量的定义,包含变化类型 Added/Updated/Delete/... 和变化和的完整对象
type Deltas []Delta
type Delta struct {
Type DeltaType
Object interface{}
}该队列是一个保存着资源变化量(Deltas)的先进先出队列,里面有两个主要存储结构:
- queue -
[]string队列的核心结构就是此 slice,里面保存着有变化资源的 key 列表,形式如 namespace/name - items -
map[string]保存变化的具体内容 map,当要从队列中 Pop 一个变化时间事,通过从 queue 的 key 从此 map 里定位到一组变化量,可能会包括多个 Added/Updated 事件等
使用上面的 DeltaFIFO 创建 Controller
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// ...
cfg := &Config{
Queue: fifo,
ListerWatcher: s.listerWatcher,
ObjectType: s.objectType,
FullResyncPeriod: s.resyncCheckPeriod,
RetryOnError: false,
ShouldResync: s.processor.shouldResync,
Process: s.HandleDeltas,
WatchErrorHandler: s.watchErrorHandler,
}
func() {
s.startedLock.Lock()
defer s.startedLock.Unlock()
s.controller = New(cfg)
s.controller.(*controller).clock = s.clock
s.started = true
}()
// ...启动 Controller
func (c *controller) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
go func() {
<-stopCh
c.config.Queue.Close()
}()
r := NewReflector(
c.config.ListerWatcher,
c.config.ObjectType,
c.config.Queue,
c.config.FullResyncPeriod,
)
r.ShouldResync = c.config.ShouldResync
r.WatchListPageSize = c.config.WatchListPageSize
r.clock = c.clock
if c.config.WatchErrorHandler != nil {
r.watchErrorHandler = c.config.WatchErrorHandler
}
c.reflectorMutex.Lock()
c.reflector = r
c.reflectorMutex.Unlock()
var wg wait.Group
wg.StartWithChannel(stopCh, r.Run)
wait.Until(c.processLoop, time.Second, stopCh)
wg.Wait()
}构造 Reflector
Reflector 的作用是维护 apiserver 的指定类型资源与本地缓(Indexer)存随时保持同步
func NewNamedReflector(name string, lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {
realClock := &clock.RealClock{}
r := &Reflector{
name: name,
listerWatcher: lw,
store: store,
// We used to make the call every 1sec (1 QPS), the goal here is to achieve ~98% traffic reduction when
// API server is not healthy. With these parameters, backoff will stop at [30,60) sec interval which is
// 0.22 QPS. If we don't backoff for 2min, assume API server is healthy and we reset the backoff.
backoffManager: wait.NewExponentialBackoffManager(800*time.Millisecond, 30*time.Second, 2*time.Minute, 2.0, 1.0, realClock),
resyncPeriod: resyncPeriod,
clock: realClock,
}
r.setExpectedType(expectedType)
return r
}Reflect 启动后,做的第一件事就是从 apiserver ListWatch 数据,把数据维护到 DeltaFIFO 队列中,然后 Controller 会进入一个 processLoop 循环从队列里 Pop 数据处理。
进入 processLoop 循环
循环从 DeltaFIFO 队列中 Pop 对象,并由 informer 中的 HandleDeltas 方法处理变化事件:
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) HandleDeltas(obj interface{}) error {
s.blockDeltas.Lock()
defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()
// from oldest to newest
for _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {
switch d.Type {
case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:
s.cacheMutationDetector.AddObject(d.Object)
if old, exists, err := s.indexer.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {
if err := s.indexer.Update(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
isSync := false
switch {
case d.Type == Sync:
// Sync events are only propagated to listeners that requested resync
isSync = true
case d.Type == Replaced:
if accessor, err := meta.Accessor(d.Object); err == nil {
if oldAccessor, err := meta.Accessor(old); err == nil {
// Replaced events that didn't change resourceVersion are treated as resync events
// and only propagated to listeners that requested resync
isSync = accessor.GetResourceVersion() == oldAccessor.GetResourceVersion()
}
}
}
s.processor.distribute(updateNotification{oldObj: old, newObj: d.Object}, isSync)
} else {
if err := s.indexer.Add(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(addNotification{newObj: d.Object}, false)
}
case Deleted:
if err := s.indexer.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(deleteNotification{oldObj: d.Object}, false)
}
}
return nil
}HandleDeltas 主要将队列中的不同的变化事件分发到两个地方
- indexer - 更新本地缓存队列
- distribute - 将时间分发到已注册的 eventHandler
至此,完整的 informer 运行架构可简单的如以下图所示
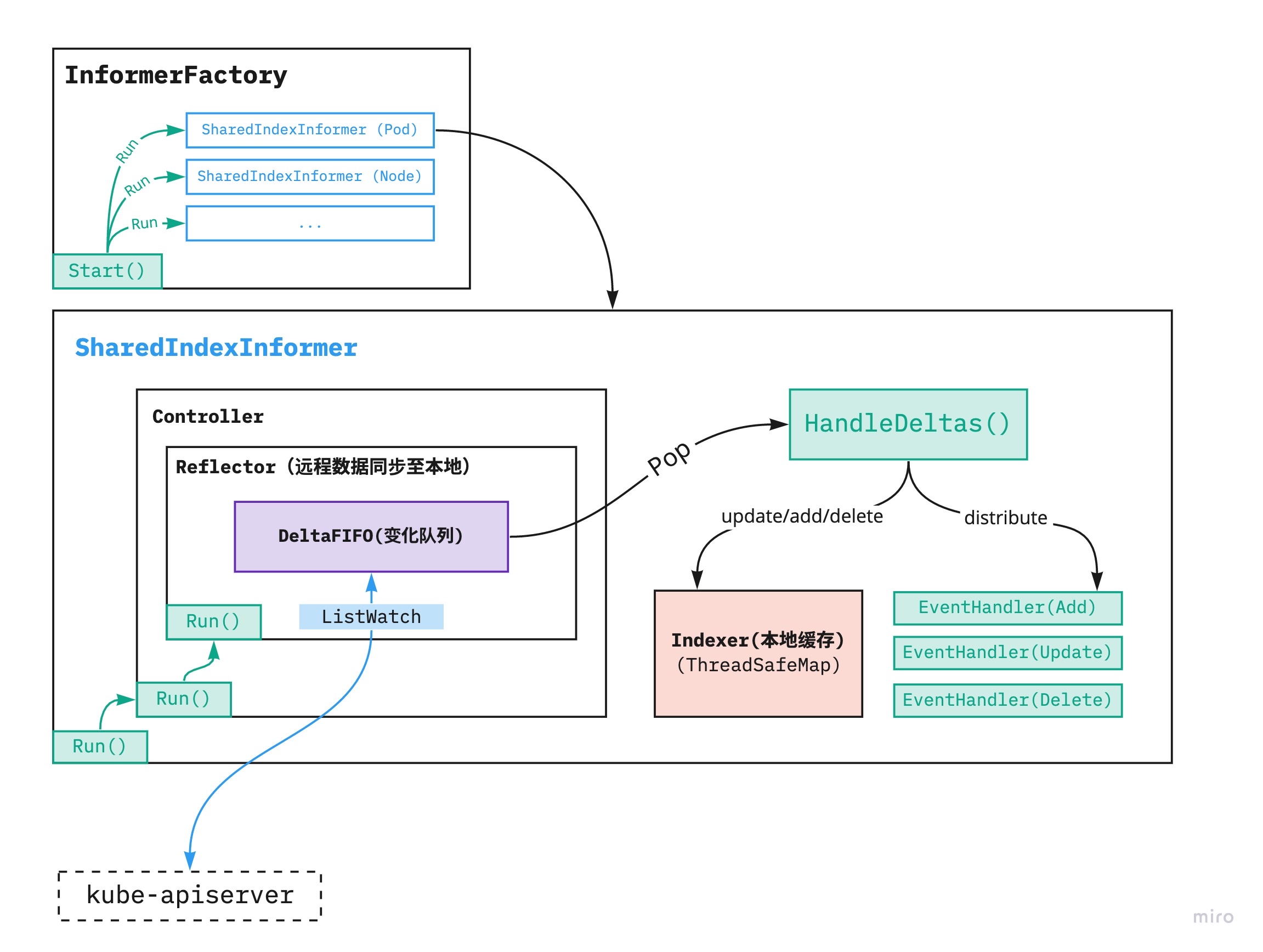
kube-controller-managet 的使用示例
具体的 controller 创建的时候传入的需要资源的 informer,构造不同的 controller 时都是从同一份 ControllerContext 中的 InformerFactory 拿到具体资源的 informer
func NewControllerInitializers(loopMode ControllerLoopMode) map[string]InitFunc {
controllers := map[string]InitFunc{}
// ...
controllers["deployment"] = startDeploymentController
// ...
}
func startDeploymentController(ctx ControllerContext) (http.Handler, bool, error) {
if !ctx.AvailableResources[schema.GroupVersionResource{Group: "apps", Version: "v1", Resource: "deployments"}] {
return nil, false, nil
}
dc, err := deployment.NewDeploymentController(
ctx.InformerFactory.Apps().V1().Deployments(),
ctx.InformerFactory.Apps().V1().ReplicaSets(),
ctx.InformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods(),
ctx.ClientBuilder.ClientOrDie("deployment-controller"),
)
if err != nil {
return nil, true, fmt.Errorf("error creating Deployment controller: %v", err)
}
go dc.Run(int(ctx.ComponentConfig.DeploymentController.ConcurrentDeploymentSyncs), ctx.Stop)
return nil, true, nil
}
// Deployment Controller
func NewDeploymentController(dInformer appsinformers.DeploymentInformer, rsInformer appsinformers.ReplicaSetInformer, podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer, client clientset.Interface) (*DeploymentController, error) {
//...Resync 机制是什么
https://github.com/cloudnativeto/sig-kubernetes/issues/11
定时将 Indexer 缓存重新同步到 DeltaFIFO 队列中,让 eventHandler 处理失败的事件能够重新处理
具体表现是使用 informer 时会定时触发一次全量的 Update 事件